It’s Official: Google Now Counts Site Speed As A Ranking Factor
Google has kept a promise it made last year: Site speed is now a ranking factor in Google’s algorithm, and is already in place for U.S. searchers. But Google also cautions web site owners not to sacrifice relevance in the name of faster web pages, and even says this new ranking factor will impact very […]
Google has kept a promise it made last year: Site speed is now a ranking factor in Google’s algorithm, and is already in place for U.S. searchers. But Google also cautions web site owners not to sacrifice relevance in the name of faster web pages, and even says this new ranking factor will impact very few queries. More on that below, but first the background on today’s announcement from Google Fellow Amit Singhal and Matt Cutts, head of Google’s web spam team.
Why Page Speed Matters
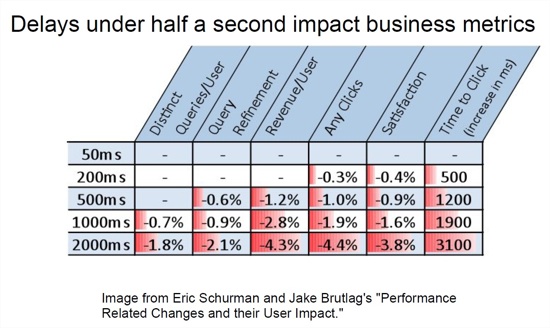
The first warning that site speed was on Google’s radar came last November, when Cutts said there was “strong lobbying” inside Google to account for site speed as a new ranking factor. Speaking at SMX West last month, Google’s Maile Ohye showed a slide indicating that delays of under a half-second impact business metrics.
In addition to the numerous studies over the years that show Internet users prefer fast pages, Singhal says Google ran its own testing on how users respond to page speed, including experiments on Google.com. Singhal and Cutts point to a June 2009 blog post on the Google Research Blog that talked about how Google purposely slowed down its search results to measure the impact on search behavior.
Our experiments demonstrate that slowing down the search results page by 100 to 400 milliseconds has a measurable impact on the number of searches per user of -0.2% to -0.6% (averaged over four or six weeks depending on the experiment). That’s 0.2% to 0.6% fewer searches for changes under half a second!
“When we slow our own users down [on Google.com], we see less engagement,” Singhal says. “Users love fast sites. A faster web is a good thing all around.”
How Google Measures Page Speed
Singhal says there are two primary ways Google will measure page speed:
- How a page responds to Googlebot
- Load time as measured by the Google Toolbar
In December, Google added a page speed report to Webmasters Tools in the “Labs” section. The report shows how fast your site loads, specifically calls out several pages on your site, and offers suggestions to improve page speed.
Where Page Speed Fits in Google’s Algorithm
Google’s algorithm has about 200 different ranking factors, and even though Google is taking the unusual step of publicly announcing a new factor, Cutts says site owners shouldn’t overestimate the impact of page speed on rankings.
“Quality should still be the first and foremost concern [for site owners],” Cutts says. “This change affects outliers; we estimate that fewer than 1% of queries will be impacted. If you’re the best resource, you’ll probably still come up.”
Singhal says the focus remains on improving the user experience on Google.com, and the company can’t do that if it gets the relevance of search results wrong. “We want to return faster sites,” he says, “but not at the expense of relevance.”
Final Thoughts
Page speed is in place now as a ranking factor on Google.com, and has been for a couple weeks. If your site was going to be impacted, it probably would’ve happened already. Google plans to monitor the results of this change and eventually expand the use of page speed as a ranking factor in other countries.
One last note: Google says this ranking change has no relation to its upcoming Caffeine rollout, which is about how Google indexes the web, not how it ranks pages.
Contributing authors are invited to create content for Search Engine Land and are chosen for their expertise and contribution to the search community. Our contributors work under the oversight of the editorial staff and contributions are checked for quality and relevance to our readers. The opinions they express are their own.
Related stories
New on Search Engine Land