How to set up and optimize your Google Business Profile
Sponsored by Semrush, written by Miriam Ellis and edited by Rebecca Kelley
Your Google Business Profile (GBP) is a listing of your business (like the one shown above) in Google’s local business index, which the general public sees in Google Search results and local Maps.
It’ll become one of your company’s most important marketing assets and customer service vehicles because of the dominant role Google has come to play in how people discover nearby resources online.
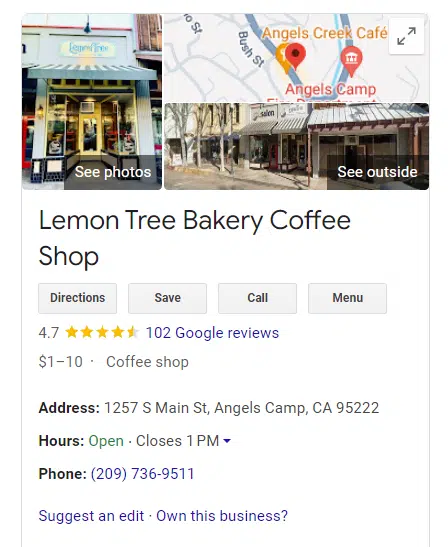
By creating your first GBP, your business can be returned as a result for any searcher interacting with Google Search and Maps, enabling potential customers to discover and choose your business.
For example, when a searcher looks for something like “cafes near me,” your GBP can be included in:
Google’s local packs
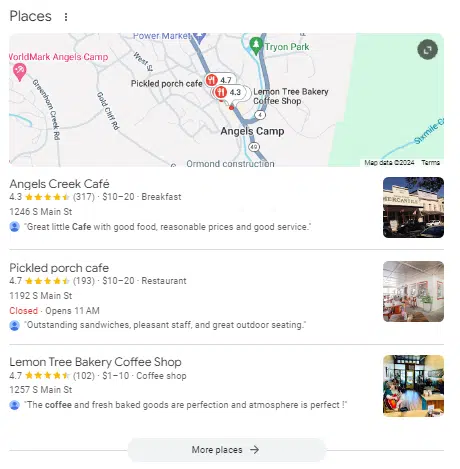
These are the main local results that turn up within Google’s organic search engine results pages (SERPs). They usually consist of three listings but can sometimes have fewer entries or also contain paid ads.
Google’s local finders
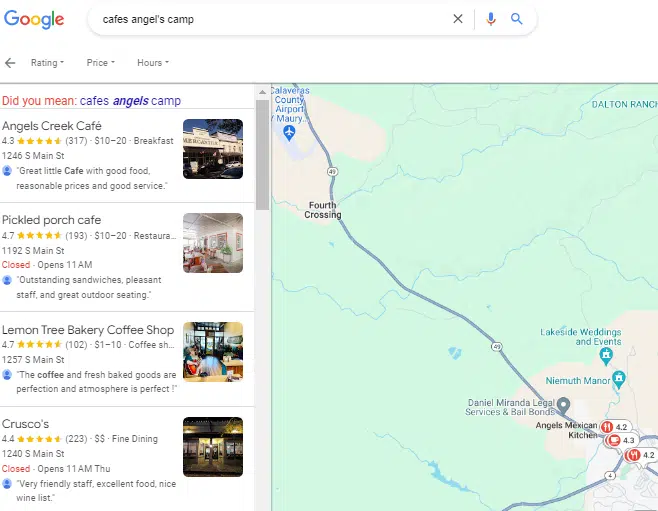
When you click on the “more places” link at the bottom of a local pack, you’ll be taken to the local finder view, which includes a map and an expanded set of listings and filter criteria.
Google Maps
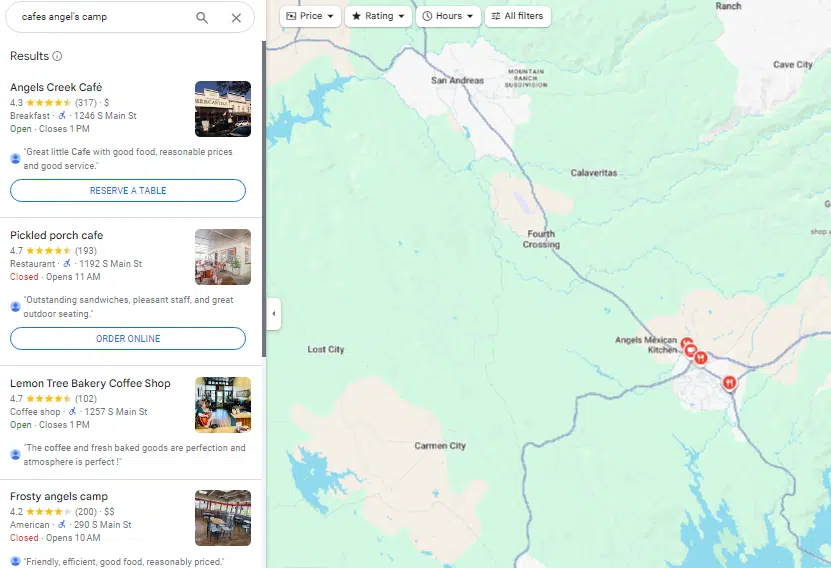
Alternatively, a user can search via the Maps link in search or on their phone and be shown Google Maps. Google Maps looks similar to the local finder view but is a different entity that can feature moderately or significantly different local business rankings and filter criteria.
Creating your first Google Business Profile is the key to unlocking visibility in all of Google’s local-related interfaces.
What you need to get started with your first GBP
Your journey begins with six vital steps.
1. Determine your eligibility
You need to be sure that your business model is eligible for inclusion in the GBP system. Go to the guidelines for representing your business on Google. Bookmark this link – it’s like the instruction manual for both creating and managing your GBP over time.
This document begins with a basic description of eligibility. You should read the entire resource in full, but to summarize:
- Your business is eligible if you serve customers face to face, either at your place of business (like a cafe) or at customers’ locations (like a house cleaning company).
- You must have an address of some kind, even if it’s only your home address.
- You must have a phone number.
- You must comply with the guidelines to avoid having your listing suspended or disabled.
If you don’t serve customers in person, you’re not eligible for a Google Business Profile and will need to look into other forms of online marketing to promote your enterprise.
Likewise, you’re ineligible if you lack an address. You must at least have a home address to create a listing.
Virtual offices and P.O. boxes aren’t acceptable as an address. If you operate in a co-working space, it must have street-level signage for your business and a direct phone number that’s staffed by someone during listed business hours.
2. Determine your business model, as Google defines it
Read through the guidelines to understand how Google defines different business models. Understanding these definitions is crucial to knowing what you are allowed to do in their system.
Your model is likely one of the following:
- A single-location, brick-and-mortar business (like a plant nursery).
- A multi-location, brick-and-mortar business (like a chain of hardware stores).
- A single or multi-location brick-and-mortar business with multiple public-facing practitioners (like a legal firm with five lawyers who serve clients face-to-face).
- A single or multi-location brick-and-mortar business with multiple public-facing departments (like a hospital with separate departments for emergency, X-ray, and obstetrics).
- A single location local service area business (like a plumber who serves customers at their homes and businesses, not at the plumber’s own location).
- A multi-location service area business (like a plumbing franchise with multiple service areas, each based around a different hub).
- A hybrid model (like a restaurant that offers both in-house dining and delivery).
- A home-based business (like a dog groomer who operates out of their home).
- A co-located brand (like a Pizza Hut and KFC sharing a single location).
- Another model like an ATM, kiosk, seasonal business, or ghost kitchen.
By reading the guidelines, you’ll find out how many GBPs you’re eligible to create and how Google wants you to fill out relevant fields of your listings. Failure to adhere to the guidelines can result in your listing being suspended or disabled.
3. Get a Google account
In order to create your first GBP, you must create a free Google account.
4. Document your core local business information
Once your Google account is live, you’ll have access to handy resources like Google Sheets.
Open a spreadsheet and accurately document the following information about your business, referring to the guidelines you’ve read to understand how to properly fill out each field:
- Your business name as it appears in the real world.
- Your complete business address.
- Your phone number.
- The date you opened your business.
- Your website address.
- Links to your social profiles.
- Your hours of operation.
- A description of your business in less than 750 characters.
Do category research
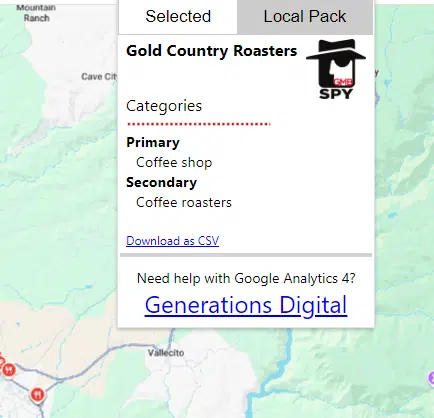
When you create your GBP, Google will allow you to select up to 10 business categories to explain your business. These categories significantly impact whether your business will be shown to searchers looking for what you offer, so they’re very important.
The first category you select will be your “primary category.” It’ll have the strongest ranking impact, but each of your categories will influence whether Google returns your listing as a result for different searches.
Because of the vital role correct categorization plays in local search rankings, it’s worth it to invest a little time in researching the categories being used by your top competitors in your town or city.
Download the free GMB Spy Chrome extension, go to Google Maps, and do some searches related to your business, like “cafe in angel’s camp” or “coffee shop near me.” Click on the top competitors and note down in your spreadsheet what you see them using as their primary and secondary categories.
The primary category you choose should be the one that best describes your overall business. For example, if you’re marketing a restaurant that specializes in Italian food, your best primary category will likely be “Italian restaurant” rather than just “restaurant.”
Be specific and use the additional categories to flesh out aspects of your business further.
5. Gather multimedia to showcase your business
Google allows you to enhance your GBP with both photos and videos. They’ll play a major role in whether searchers find your business appealing and choose it for a transaction.
Read Google’s technical specifications for GBP photos and videos so that you understand formatting requirements.
At the bare minimum, gather the following photos:
- If you’re marketing a brick-and-mortar business, show at least one clear exterior and interior shot of the business.
- If you’re marketing a service area business (SAB), photograph company vehicles, uniformed staff, or some other aspect of your business that proves its legitimacy as a real company.
You should also plan to add as many high-quality photos as possible over time of any of the following:
- Individual goods and services.
- Shelfies (photos of inventory on shelves).
- Before-and-after photos of completed projects.
- Amenity photos of features such as patio dining, parking, ADA access, restrooms, etc.
- Staff photos.
- Seasonal photos.
Your listing will be further enhanced if you create and upload guideline-compliant videos of your premises, projects, staff, events, and other features.
How to create your Google Business Profile
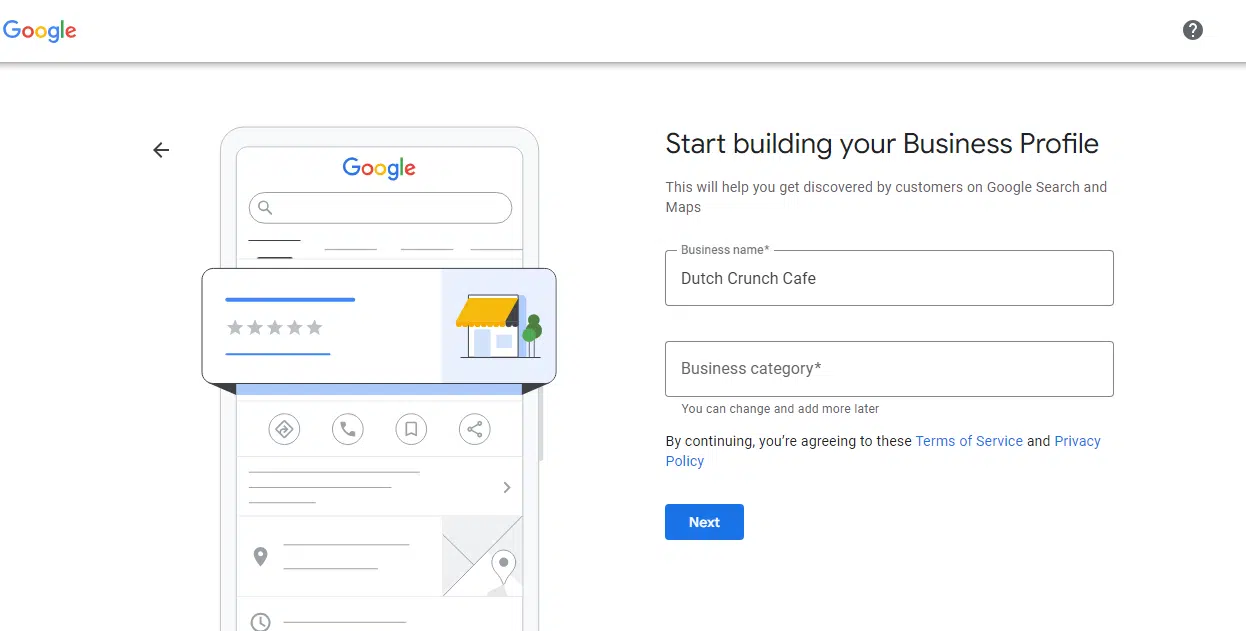
While signed into your Google account, start creating your first Google Business Profile here.
Google will first ask you to enter your business name so that they can be sure that a listing doesn’t already exist for your business.
You’ll then be taken to a screen like the above, where you’ll begin by entering your business name and the primary business category you identified in your research.
Hitting the “next” button will begin walking you through the listing creation wizard so that you can fill out all of the fields you’ve entered into the spreadsheet you’ve created.
While it’s always possible to go back and edit your listing once it’s live and verified, it’s better to get your core details right the first time.
If you’re unsure how to best fill out a specific field in the wizard, refer back to the guidelines for representing your business on Google to ensure you comply with Google’s policies and avoid penalties.
Here are a few rules you should keep in mind as you’re creating your first GBP:
- Be sure your business name reflects your real-world street signage and the way you answer your phone. Don’t add extraneous keywords. Adhere to any guidelines that apply to your model.
- If you’re a service area business, like a plumber or landscaping service, Google wants you to select the options that indicate you don’t serve customers at your place of business. This will result in your street address being hidden in Google’s local results. Unfortunately, multiple studies like this one have demonstrated that complying with Google’s hide-address rule frequently results in SABs ranking lower than competitors who have brick-and-mortar locations. Because of this, it’s a goal for most SABs to eventually rent at least one small staffed location so that they’re no longer disadvantaged in the local results.
- Be sure your hours of operation are accurate. If your business has complex open hours, read Google’s documentation on how to properly reflect this in their system.
Once you’ve filled out all the fields and submitted your listing, you’ll be prompted to proceed to the next verification step. Resist the urge to make any further edits to your GBP until you’ve completed the verification process.
How to verify your Google Business Profile
Verifying your listing lets Google know that you’re authorized to represent the business for which you’ve created a GBP.
Start by reading through this Google document regarding all the types of verification they offer, but know that these days, video verification tends to be Google’s most common route. Via this methodology, you’ll be uploading a video to prove to Google that your business is legitimate.
Follow these crucial do’s and don’ts in your GBP verification video:
Don’t:
- Film other people’s faces, private information about yourself or others, or any sensitive information like your bank statements or tax ID.
- Make your video shorter than 30 seconds or longer than five minutes; the best practice is to keep it under two minutes.
- Make an edited video – it needs to be a continuous recording without breaks.
- Try to film without practicing first.
Do:
- Record your video and upload it with a mobile device, following these steps.
- If you’re verifying a brick-and-mortar business, your video must feature:
- The location of your business.
- Official street and number signs.
- Neighboring businesses.
- Nearby landmarks or the area around your business.
- Your business storefront.
- Showroom.
- Permanent signage, such as on a signboard or window.
- Proof that you’re an authorized representative of the business (this can be proven by recording yourself unlocking the store, opening a cash register, using a point-of-sales system, or unlocking other areas such as a staff room or storage area).
- If you’re verifying a service area business, your video must include:
- Signs in your service area that advertise your business (like billboards) or street signs and landmarks near your business.
- Footage that proves your business exists, such as branded vehicles, equipment, or apparel.
- Footage of business documents such as invoices or bills that feature the name on your GBP.
- Record at the lowest-quality settings to reduce the file size to prevent Google from rejecting it.
It’s important to know that video verification is notoriously buggy. If you experience problems, watch this troubleshooting video from Darren Shaw of Whitespark.
If you don’t find an answer to your issue in that video, go to the Google Business Profile Help Community to document the problem in hopes that a volunteer Product Expert can help you troubleshoot.
Google’s review of your video can take at least five days, but once you’ve achieved verified and live status, you’re ready to start making the most of your GBP.
Optimizing your Google Business Profile
Once your profile is live, you’ll be able to manage most aspects of it by looking up the name or name/city of your business in Google’s main search engine.
This should bring up a management interface commonly known as the “New Merchant Experience” (NMX), which looks like this:
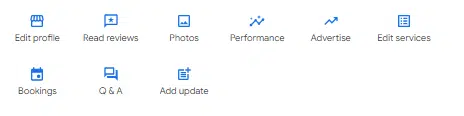
Your Google Business Profile is not a set-and-forget listing. It is a major marketing asset that requires ongoing management to deliver maximum traffic, clicks, conversions, and sales.
Nearly a dozen aspects of your GBP are strongly believed to impact its rankings within Google Search and Maps.
While the algorithm via which Google calculates relevance is proprietary, you should pay special attention to the ranking aspects of the following fields:
Business name
Business names that contain words that match search language frequently rank higher than competitors whose names don’t contain any element of the search term.
For example, a business named “The Gluten-Free Bakery” is likelier to rank well for a searcher looking up gluten-free bakery near me than a business named “Carl’s Place.”
Google’s bias toward keywords in the business name sometimes causes local businesses to get a DBA to change their name to legitimately reflect a more optimized title.
Categories
if you miscategorize your business, it won’t show up well for searchers seeking goods and services related to appropriate categories.
From time to time, you should re-run your research on the categories your top competitors are using to see if you need to edit yours.
Address
This may be the greatest factor in determining which searches you rank well for. Google shows each searcher different local packs, finders, Maps, and organic results based on their physical location at the time they search.
If Google considers your business to be outside the imaginary radius they draw around each searcher, they may not show your listing as a result for that person.
Sometimes, a local business may discover that their location is holding them back from being visible to the searchers they need to connect with.
For example, if your business is located just outside the borders of a city, Google may not show you to searchers inside that city.
While building up the authority and optimization of your listing can sometimes overcome Google’s bias concerning your location, some businesses realize that they must relocate to become central to a specific geographic market.
Website Link
The optimization and authority of the website page you link to from your Google Business Profile will influence its rank.
Most single-location businesses link to their home page because it has typically built up the greatest authority due to the links and mentions it’s earned over time.
In other scenarios, a multi-location, multi-practitioner, or multi-department model will choose to link to landing pages on the site to provide a better user experience to someone clicking from the GBP to the company’s website.
Overall, part of optimizing your GBP is building an authoritative website that will contribute to your listing’s ability to rank well in Google’s local interfaces.
Hours of operation
Google prefers to show users businesses that are open at the time of search.
You can optimize your hours of operation by auditing when your local competitors are open to see if you can add or change your schedule so that you’re open when others are closed, giving you a ranking advantage.
Reviews
The number of reviews you receive from the public and the overall average of your reviewers’ star ratings will impact your local rankings.
Be wary of thinking of this as a numbers game, however. While the local SEO industry has long observed that you appear to receive a local ranking boost once you receive your first 10 reviews, it doesn’t follow that you get additional boosts at any subsequent benchmark.
Your goal should be to steadily earn and then surpass the number of reviews that have been achieved by your top local competitors. The velocity at which you receive new reviews may also impact rank, as may the date on which you last received a fresh review.
Reviews are one of the most influential aspects of your GBP. They’re like a free sales force for your business. However, they’re a marathon, not a sprint.
By offering excellent customer experiences, responding to all the reviews you receive, and setting up a formal review acquisition process, your goal can be to steadily earn a slow drip of high-star reviews week after week, month after month, for the life of your business.
Read Google’s prohibited and restricted content policy to be certain you’re strictly adhering to their review guidelines.
Attributes
The NMX “more” tab includes fields for you to select attributes such as “identifies as Latino-owned” or “small business” if they’re relevant to your business. These attributes can help you show up for searchers who include such qualifiers in their search language.
However, there are two options you should avoid selecting: “offers online appointments/estimates” and “onsite services.” Why? Because you can’t remove them once activated, and because they seem to override any of the other text snippets known as local justifications that can enrich your local pack listings.
Products
If you sign up for Google’s Merchant Center, your Google Business Profile can feature a “See What’s In Store” section displaying your inventory. This can help you rank for relevant product searches.
Services
Be sure to add every relevant service in the “Add Services” section of your NMX, as these have a demonstrable ranking impact.
Popular times
Just as hours of operation impact local rankings, Google’s concept of your most popular times may influence them to rank your business more highly during those hours.
Think of special offers you might make, such as a happy hour or senior shopping morning, to help your business have a notable popular time.
Menu items
The items on your menu can help you rank more highly for searchers seeking specific goods.
In addition to the above fields, place a priority focus on the following:
Images
Google can change the photos they show on your listings based on searcher language.
For example, someone looking for “burritos near me” can be shown a different image than someone searching for “tacos near me” if your business takes the time to upload high-quality images of both dishes.
Make it a goal to photograph every possible aspect of your business over time so that an influential photo is always available to tell a potential customer that you have what they’re seeking.
Review responses
Every time you respond to a review, it’s a signal to the public that your business is responsive and takes good care of the public.
When you receive legitimate complaints, do everything you can to make it right for the dissatisfied customer. Not only does this demonstrate your company’s accountability, but a skilled response to a negative review can often win back the customer and inspire them to edit their review and improve the rating they initially gave you.
Google Questions and Answers
The Q&A tab of your NMX is one that you’re allowed to populate with the FAQs you know your business receives.
For example, you might frequently be asked if you’re open on a particular holiday or stock a certain product. As the business owner, you can both ask and answer these questions.
Additionally, the public can use this functionality to ask you questions. Respond quickly to any queries you receive. If you don’t answer questions, your potential customer may receive incorrect replies from members of the public, who are also allowed to respond to this section of your GBP.
Apart from these three fields, your brand may also want to experiment with the microblogging functionality in your NMX labeled “Add Update,” formerly known as Google Posts. You can find complete information about this interesting feature in this Google document. Use of it can help your listing stand out from less-motivated competitors as you promote news and special events.
Google updates work well for some businesses, but it’s important to know that there’s debate over whether Google will keep this feature long-term. You may be better off linking to your social profiles and investing time in building up your social media content instead.
A good rule of thumb is to explore any field Google offers you to see if it’s relevant and useful to your business. Google regularly debuts and removes GBP features, so don’t put all your marketing eggs in one basket by becoming too dependent on a single feature.
Experiment with any opportunity to offer further details about your business or be more interactive with potential customers.
Tracking GBP performance
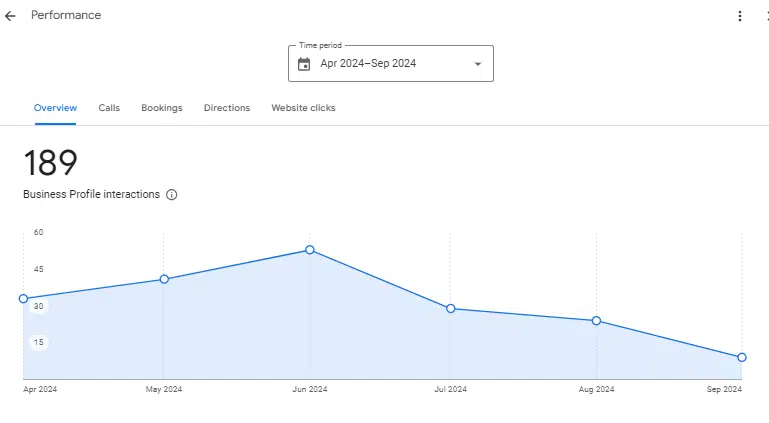
By clicking on the “Performance” link in your NMX, you’ll be able to access the simple analytical data Google gives you about your listing. This includes:
- How many people view your listing.
- A sampling of search terms that cause your listing to be shown.
- The devices and platforms people use to find your listing.
- The number of people who click to call you from your listing.
- The number of people who request driving directions from your listing.
- The number of people who click on your website from your listing.
You can think of these insights as both a free health check on your listing and a basic way to test whether something new you’ve added or changed about your listing appears to have caused either upward or downward movement in these figures.
For professional-level analytics, you may want to invest in a tool like Semrush, which enables you to track both local and organic rankings.
You may also want to learn the art of UTM tagging to track the performance of different parts of your GBP via Google Search Console, a free source of further analytical data you can get to know.
The more competitive your market or complex your business model, the more time and money you should expect to invest in becoming skilled at utilizing analytics programs and software to gain strategic insights into how the public is interacting with your website and listings. If SEO and analytics are all new territory for you, get a free crash course here.
Understanding common GBP problems
There are too many documented problems associated with Google Business Profiles to cover in a single article, but here are four you need to know about when creating your first listing.
Mistaken perceptions of GBP
Even after you’ve verified your listing, it’s important to understand that it doesn’t belong to your business.
All GBPs belong to Google. They can edit them at any time and accept editing suggestions from the public.
Business owners frequently feel frustrated when they realize that Google considers these impactful listings to be open-source documents that anyone can attempt to contribute to and even steal.
It’s completely understandable to want to have total control over your online presence. Your livelihood depends on your business, after all. But it’s vital to understand that you’re on Google’s property while managing your GBP.
You’re a renter rather than an owner, and there will be times when you may become exasperated by a policy of Google or a lack of response on their part to a problem. You may wish that things were different, but accepting the reality of how Google’s local system works will set correct expectations for your brand.
Ranking problems
Every local business wants to rank as well as possible in Google’s local packs, finders, and Maps.
While there are no fixed number-one local rankings, because Google tailors their results around the location of each searcher, you’ll be investing a lot of time in figuring out how to increase your visibility for a variety of search phrases.
In some cases, you’ll run up against a keyword phrase for which you seem to be either stuck way down in the rankings or even invisible. This is the point at which you’ll need to start learning about how to do a formal audit of your competitors to try to understand why you are being outranked.
Here are a few questions to begin troubleshooting with:
- When I look up my city on Google Maps, is my location inside or outside the red border? If outside, this may be my barrier to ranking.
- Have I chosen the right categories to let Google know my business is relevant to a particular search phrase? If not, can I add a new category to help?
- Am I located within the same building or even within a few blocks of a competitor who shares my categories, causing Google to filter out my business in favor of theirs and making me invisible unless I zoom in on the map? If so, I’ll need to strengthen every aspect of my listing and website to prove to Google that I’m the business that should be shown instead of filtered out.
- Am I adhering to the guidelines? If not, I might be penalized.
- Are the businesses outranking me for this search term doing so because they’re spamming Google (for example, they’ve stuffed extraneous keywords in their business names)? If so, I can report them to Google and hope to move up in the rankings.
Each time you encounter a new ranking mystery, look it up via Google Search and see what others say about similar scenarios. If you can’t find a good answer, you may need to hire a local SEO consultant or agency for professional troubleshooting.
Spam problems
Unfortunately, weaknesses in Google’s local system enable spammers and scammers to take advantage of Google Business Profiles in various ways.
For example, spammers can:
- Keyword stuff business names.
- Move your map pin.
- Hijack your listing, redirecting its phone number or website links to their own.
- Write fake reviews of your business and leave you low-star ratings.
- Leave ratings that are slightly lower than your average to erode your overall rating.
- Report your business as closed.
- Create listings for fake businesses.
This is just the tip of the iceberg of all the things bad actors do in Google’s system, and some industries are particularly polluted with spam.
If you notice that a listing outranking yours looks suspicious (for example, it has a keyword-stuffed name, or its address is actually a vacant lot), or you become the subject of a review spam attack, Google has various methods for reporting these issues.
These methodologies change frequently, so it’s best practice to look them up when you experience them to see what recent documentation and sources say.
It’s important to have realistic expectations about GBP spam: it’s everywhere, and Google can’t catch it all. Resolve to deal with each problem as it arises.
Penalties
Your listings can become suspended or disabled if:
- You accidentally violate the guidelines and get caught.
- You get mistakenly swept into a cleanup Google has undertaken in a particular industry or market.
- A member of the public reports you to Google for an apparent problem.
These penalties can sometimes occur through no fault of your own, and the notice from Google that your GBP is suspended or disabled can come as an unwelcome surprise.
It’s important to know these terms:
- A disabled listing is still visible to the public but has become unverified. You can’t respond to reviews or write Google posts while your listing is in this state. This status is sometimes referred to as a “soft suspension.”
- A suspended listing is not visible to the public. It’s been removed from Google Search and Maps. This status is sometimes referred to as a “hard suspension.”
In both scenarios, you’ll need to go through the appeals process in hopes of being able to get back into Google’s good graces, recover your verified status, and hopefully regain access to the management of your listings.
The future of GBP
Google has invested heavily in the local index over the years and will likely continue encouraging businesses like yours to list on their platform.
At present, a hot topic is the extent to which Google may integrate AI into its local search results, and the company is continuously experimenting with new features.
It’ll be core to your local search marketing strategy to keep up with the news of Google developments so that you can recognize emerging opportunities.
You can bookmark this publication and follow local SEOs on social media to stay informed. Your curiosity and willingness to try new things will serve you well in the GBP environment.
By completing yours correctly from the start and committing to responsiveness to reviews and questions, your GBP will become an always-on testament to your devotion to serving your local community.
Keep reading for some of the most common questions about Google Business Profiles, or stay up to date with the latest GBP news.
New on Search Engine Land