Disavowing backlinks: How to safely remove toxic links for SEO
Discover how disavowing backlinks can protect your site from SEO penalties. Learn best practices, common pitfalls, and how to identify harmful links quickly
If getting all the traffic from Google search results you can is at the top of your priority list, you’re probably keen to meet or exceed all of Google’s guidelines.
The one on that list that’s the most talked about but that not everyone fully understands? Backlinks.
Backlinks are hyperlinks from one website to another that signal trust, authority, and relevance to search engines.
So, if another website links to yours, you have a new backlink.
Backlinks can improve a site’s search engine optimization (SEO) by passing link equity (like a positive vote for your site), helping it rank higher in search results. Quality backlinks from reputable sites are widely accepted as a key factor in Google’s ranking algorithm.
In fact, Google mentions backlinks (and refers to them as “votes”) in their philosophy:
“Google search works because it relies on the millions of individuals posting links on websites to help determine which other sites offer content of value. We assess the importance of every web page using more than 200 signals and a variety of techniques, including our patented PageRank™ algorithm, which analyzes which sites have been “voted” to be the best sources of information by other pages across the web.”
However, malicious or spammy sites (sites that are out to steal data, distribute malware, or use deceptive tactics to get traffic) can just as easily link to your site as the good and honest ones can. You can even fall victim to a spam attack, where spam links are built pointing to your site in an attempt to demote it in search results.
Say you’re a local business. Getting a link from your local chamber of commerce website would be a great, positive backlink. Getting a link from a random online directory that keyword stuffs or uses bots to build thousands of links in blog comments and on forums in order to get more traffic would be a spammy backlink.
What’s the best SEO tactic you can utilize to get rid of those links? Link disavowal.
Fortunately, there’s a tool site owners like you can use to “disavow,” that is, tell Google to ignore those malicious links, which effectively removes them from your backlink profile. We’ll take a look at that in just a bit.
But then the questions are:
Should you disavow bad links? Is it a “good” SEO tactic to use? If so, how do you disavow them?
Let’s find out.
What is link disavowal?
Link disavowal is the process of telling Google to ignore specific backlinks that may harm your website’s SEO.
Done only when your site has received, or is likely to receive, a manual action (penalty) from Google, submitting a disavow file in Google Search Console signals that your site does not endorse the spammy or low-quality links leading to it.
To disavow those low-quality backlinks, you can use Google’s Disavow Links Tool to upload a list of links to disavow. But, more on that later.
The SEO toolkit you know, plus the AI visibility data you need.

What’s the Disavow Tool?
Google’s Disavow Tool was created by Google and released in 2012 in response to the Penguin update. The Penguin update was an algorithm change launched to penalize websites using manipulative link-building tactics to boost rankings, encouraging sites to focus on high-quality, relevant content and ethical SEO practices.
Before the update was rolled out, it was possible to gain higher rankings by participating in a few unethical and manipulative link-building techniques called “link schemes.”
Link schemes are manipulative practices used to artificially boost a site’s search rankings by acquiring or exchanging backlinks. These include buying links, excessive link exchanges, or using automated programs. Google considers link schemes a violation of its Webmaster Guidelines and penalizes sites that use them.
After the Penguin update was released, Google wanted to help webmasters avoid those penalties from harmful or spammy backlinks they couldn’t control, and also to give sites who had participated in link schemes—before it was fully recognized as a no-no—a way to fix what they’d done. So, it released the Disavow Links Tool.
With the Disavow Links Tool, you can upload a list of your backlinks that you want Google to ignore in order to keep your site’s SEO squeaky clean and your rankings up.
When should you disavow links?
You should disavow links only when your site has received or is likely to receive a manual action penalty from Google. A manual action penalty from Google is applied when a human reviewer determines a site violates Google’s Webmaster Guidelines. This penalty can lower your search rankings or remove your pages from search results entirely.
In most situations, though, Google is able to identify spammy sites using a combination of automated algorithms and manual review processes and ignore the unwanted links to your site from them on its own, so you won’t receive a manual action penalty and do not need to submit a disavowal file.
To find out if you have a manual action, open Google Search Console and navigate to “Security & Manual Actions” > “Manual actions”:

If you don’t have a manual action, you’ll see a green check mark with a “No issues detected” message:

Do disavow backlinks if:
- Your Search Console shows a manual action penalty
OR - You’ve taken part in a link scheme or paid for link building that resulted in a large number of low-quality backlinks that you believe will trigger a manual action
OR - You’re the victim of a spam attack, where an attacker built many spammy links to your site in an attempt to demote your site in search results
If any of the above apply to you, try reaching out to the spammy websites first with a link removal request according to Google’s guidelines.
If they don’t respond, you can submit a disavowal file.
Do NOT disavow backlinks if:
- Your Manual actions report shows a “No issues detected” message
AND - You haven’t taken part in a link scheme
AND - You haven’t been the target of a link spam attacker
In general, you do not need to disavow backlinks unless you have a large number of low-quality backlinks and have a manual action penalty. Disavowing backlinks should always be your last resort.
Why?
Every website on the internet will end up with spammy or low-quality backlinks here and there. Google is good at ignoring them and not penalizing you, so unless this happens on a large scale, you do not need to disavow backlinks.
Disavowing backlinks can be a little bit risky. If you accidentally disavow a few legitimate links, for instance, you could end up hurting your SEO rather than helping it.
How do I identify toxic backlinks?
If you need to determine which of your backlinks are toxic and submit them to disavow (or if you’re just curious and want to know if you have any), the best way is to use a tool like Semrush or Google Search Console (GSC) to detect unnatural anchor text, sudden spikes in link volume, or links from sites with malware or adult content.
For example, the Backlink Audit tool breaks your links down into three categories: Toxic, Potentially toxic, and Non-toxic.
Links are classified as toxic or spammy based on criteria like low domain authority, irrelevant or foreign-language content, excessive exact-match anchor text, links from link farms, penalized sites, or automated link-building patterns.
To find the report, hover over the SEO icon and click “Backlink Audit”:

Now, you’ll see a backlink report showing any links the tool has identified as toxic:

You can also find your backlinks in your Search Console dashboard under the “Links” tab:
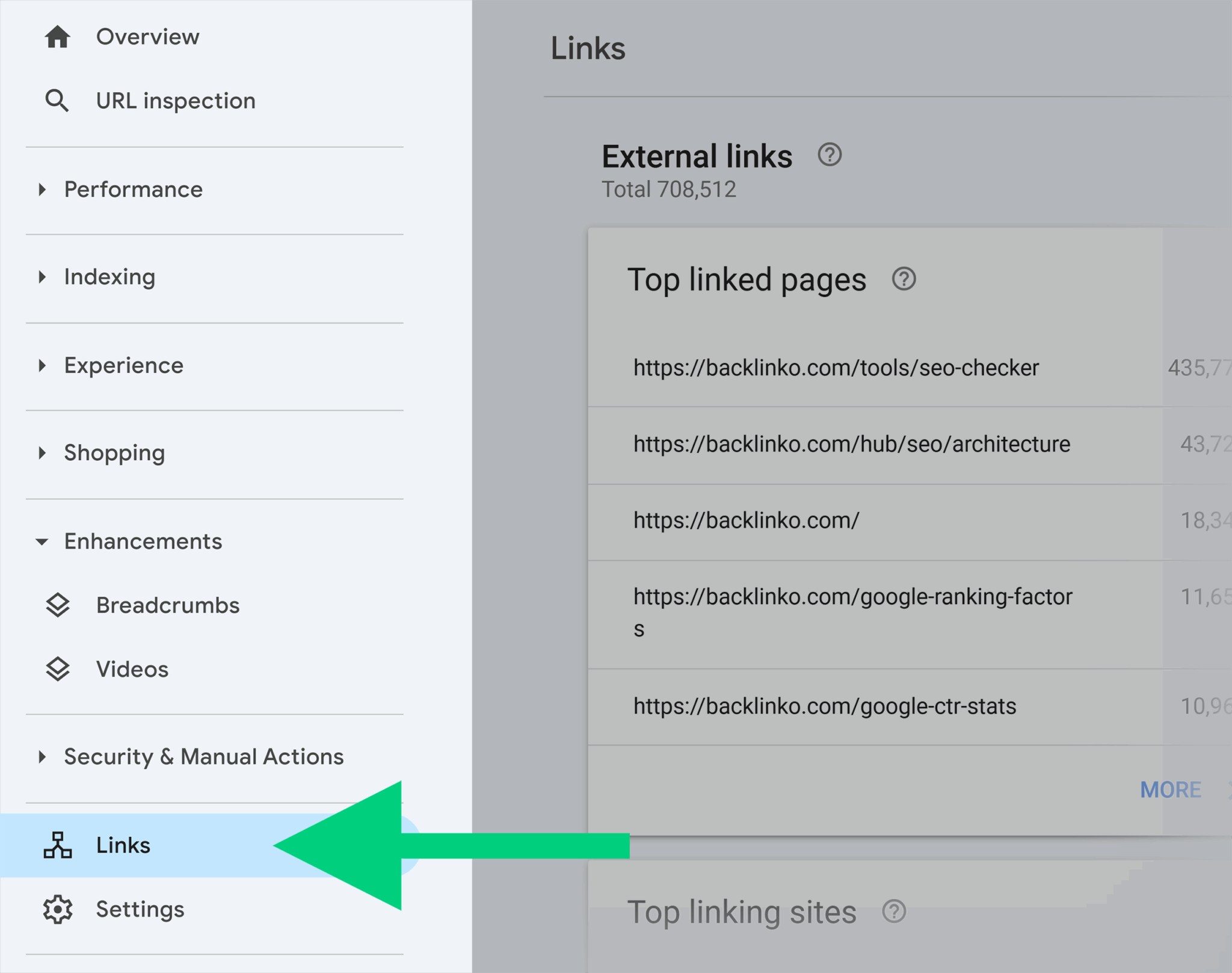
When looking for toxic links, keep an eye on the domains that have the most links pointing to your site (under “Top linking sites” in Search Console) and backlinks with spammy anchor text unrelated to your niche (under “Link text” in Search Console).

Checking links manually can be very time-consuming and difficult, which is why we always recommend using a tool.
Dig deeper: Toxic Backlinks: What They Are & How to Find Them
What is a disavowal file?
If you run a backlink audit and you find that you do have a manual action penalty or a large number of toxic backlinks and you think you’ll be penalized, the proper next step is to submit a disavowal file to Google.
A disavowal file is a text (.txt) document submitted to Google Search Console that lists backlinks a site wants to ignore. This text file tells Google not to consider specific links in ranking calculations, helping prevent SEO penalties from spammy, harmful, or unnatural link profiles.
In the document, you should list every domain or URL on their own line. Many text editor tools such as Google Docs, TextEdit on Mac, and Notes on Windows can export docs in .txt format.
To disavow pages, include the complete URL.
To disavow full domains, write it out as “domain:spammysite.com.”
For example:
https://spammysite.com/this-is-a-toxic-site
https://toxiclink.com/spammy-page
domain:harmfulsite.com
domain:badbacklinks.com

For the full guidelines on creating your disavowal file, check out Google’s guidelines.
How do you disavow backlinks?
To get started disavowing backlinks, the first thing you need to have is a URL prefix property in Google Search Console.
If you use a Domain property (which is actually recommended), you’ll have to create a URL prefix property in addition to it. Google’s Disavow Tool only works with URL prefix properties

For a full tutorial on creating Domain vs. URL prefix properties, see the 2025 Google Search Console Guide.
Go ahead and use your full URL with https and www added.
Like this:
https://www.yoursite.com
If you need more help verifying your ownership, see Google’s help page.
Once your URL prefix property is verified, navigate to https://search.google.com/search-console/disavow-links.
Next, choose your URL prefix property from the dropdown:

The button to upload your .txt file will be available:

Click the button and choose the file from your computer to upload. Once it uploads, GSC will read the list and display the number of domains and URLs you’ve disavowed:

That’s it, you’ve just disavowed backlinks to your site. It’s important to note that it takes some time for Google to process and act on your disavowal.
That’s what we’ll go over next.
Measuring your disavowal’s impact and results
So, how long does it typically take disavowed links to be ignored by Google?
According to Google, “it can take a few weeks to incorporate your list into the index as Google recrawls the web and reprocesses the pages.”
The timing depends on crawl rates and indexing frequency. Changes are not immediate, but once processed, disavowed links are excluded from future ranking evaluations.
However, note that even after your links are disavowed, it can take a few months for your changes to take effect and for the search engine results pages (SERPs) to change.
But how will you know if your link disavowal helped your site?
Track, optimize, and win in Google and AI search from one platform.

Here are a few metrics to keep an eye on:
1. Manual action penalty
If you had a manual action applied, the first and most obvious place you’ll see results is in your Search Console dashboard. Hopefully, the penalty notice will disappear and you’ll get the green check mark instead.
If that doesn’t happen, you’ll want to submit a reconsideration request by clicking the “Request Review” button:

Then, check that all the issues were fixed, write out an explanation of what you did, and click “Submit Request”:

2. Organic rankings + clicks
Where you rank in the SERPs can be a good indication of whether or not your toxic backlinks are disavowed.
Use a tool like Semrush, Google Analytics, or Search Console to monitor keyword rankings and clicks.
For example, if you have Semrush, head to the “SEO” tab then “Position Tracking” to keep an eye on rankings for your top keywords:

Pro tip: Use this free keyword rank tracker tool to quickly look up keyword rankings.
3. Organic traffic
If your site is suffering from a manual action, your organic traffic may go down to zero (or close to it). If you start to see it bouncing back, chances are your link disavowal is working.
To check organic traffic, open Google Analytics and head to “Acquisition” > “Traffic acquisition”:

From there, find Organic Search in the table. Note that you can check the “Organic Search” checkbox and uncheck the other channels to see a line graph of your traffic. This will help you better see any trends:

4. Toxicity score
Keep an eye on your “Overall Toxicity Score” in the Backlink Audit report:

What about good backlinks?
Now that you understand “bad” backlinks, what about good ones?
Getting more good backlinks is an SEO tactic that you can—and should—use to help your website rank higher in search and show up more in AI Overviews. But how do you build them? What exactly are “good” backlinks? How much will they help your site’s rankings?
To find out, check out Types of backlinks explained: How to drive SEO, traffic, and authority.


